Have you ever heard about Body Mass Index (BMI) and wondered why it’s so frequently discussed in conversations about health and wellness? Let’s delve into the realm of BMI, exploring its origins, significance, impact on health, and practical implications for individuals seeking to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Introduction
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measurement that helps assess weight in relation to height, providing valuable insights into an individual’s overall health status. This simple yet effective tool allows us to understand the significance of maintaining a healthy BMI and its impact on our well-being.
BMI serves as a key indicator for assessing weight and health, enabling us to determine whether we fall within a healthy weight range or if we are at risk of potential health complications. By considering both weight and height, BMI takes into account the relative proportions of our bodies, offering a holistic perspective on our physical condition.
Maintaining a healthy BMI is crucial for numerous reasons. Firstly, it serves as a vital gauge in preventing weight-related health issues such as obesity, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. By consistently monitoring our BMI, we can proactively address any potential risks and take necessary steps to maintain optimal health.
In essence, understanding the concept of BMI and recognizing its relevance in assessing weight and health empowers us to take charge of our well-being. By striving to maintain a healthy BMI, we can promote longevity, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and enjoy an improved quality of life. Let us delve deeper into the significance of BMI and explore how it can positively influence our overall health journey.
Understanding BMI
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a measure that helps assess an individual’s body weight in relation to their height. It provides a numerical value that indicates whether a person falls within a healthy weight range or if they are underweight, overweight, or obese. Calculating BMI is relatively straightforward, as it involves a simple formula that considers both weight and height.
To calculate BMI, divide an individual’s weight (in kilograms) by the square of their height (in meters). The formula can be expressed as BMI = weight (kg) / height^2 (m^2). For instance, if a person weighs 70 kilograms and their height is 1.75 meters, their BMI would be calculated as follows:
BMI = 70 kg / (1.75 m)^2 = 22.86
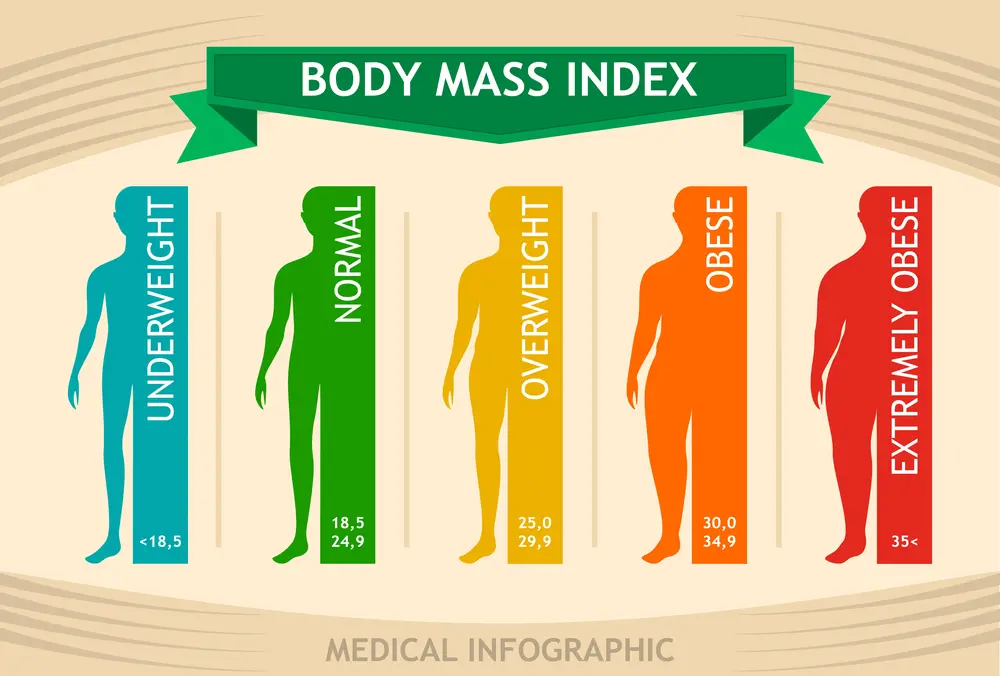
Once we have obtained the BMI value, it is important to understand the different categories associated with it. These categories provide a general guideline for interpreting the BMI value and determining whether it falls within a healthy range. The following are the commonly recognized BMI categories along with their corresponding weight ranges:
1. Underweight: BMI less than 18.5 – This category suggests that an individual’s weight may be insufficient in relation to their height. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to address any underlying concerns and ensure a healthy weight gain.
2. Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 – Falling within this range indicates a healthy weight proportionate to height. It is generally associated with a lower risk of weight-related health issues.
3. Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9 – Individuals in this category may have excess weight in relation to their height. It is essential to adopt lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, to manage weight and reduce the risk of developing obesity-related conditions.
4. Obesity: – Class I: BMI between 30 and 34.9 – Class II: BMI between 35 and 39.9 – Class III: BMI 40 or higher – These categories indicate varying degrees of obesity, with Class III representing severe obesity. It is crucial to seek medical guidance and implement comprehensive strategies for weight management and overall health improvement.
Understanding the different BMI categories and their corresponding weight ranges allows individuals to assess their own weight status and make informed decisions about their health. It is important to note that while BMI is a useful tool, it does have limitations, as it does not take into account factors such as muscle mass or body composition. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals can provide a more comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s overall health and well-being.
The Significance of BMI
BMI plays a crucial role in assessing overall health and serves as an essential tool in understanding the relationship between weight and potential health risks. By examining the connection between BMI and various health conditions, we can gain valuable insights into the importance of maintaining a healthy BMI for overall well-being.
First and foremost, BMI provides an initial indication of the potential health risks associated with weight. Research from reputable sources, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), consistently highlights the link between BMI and the development of chronic diseases. High BMI values have been associated with an increased risk of conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, certain types of cancer, and musculoskeletal disorders.
Being overweight or obese can lead to an imbalance in metabolic processes, affecting vital organs and systems within the body. Excess weight puts additional strain on the cardiovascular system, leading to an elevated risk of heart disease and stroke. Furthermore, obesity is a known risk factor for insulin resistance, which can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. The accumulation of fat in the abdominal area, often seen in individuals with higher BMIs, has been specifically linked to an increased risk of metabolic disorders.
Moreover, maintaining a healthy BMI is essential for musculoskeletal health. Excess weight can exert pressure on joints, leading to conditions such as osteoarthritis. By keeping BMI within a healthy range, individuals can reduce the strain on their joints, enhance mobility, and reduce the risk of developing debilitating conditions.
It is worth noting that BMI is not a definitive diagnostic tool, as it does not account for factors such as muscle mass or body composition. However, it serves as a valuable screening tool for identifying individuals who may be at a higher risk of weight-related health issues. Healthcare professionals can then conduct further assessments and provide personalized recommendations based on an individual’s unique circumstances.
BMI and Weight Management
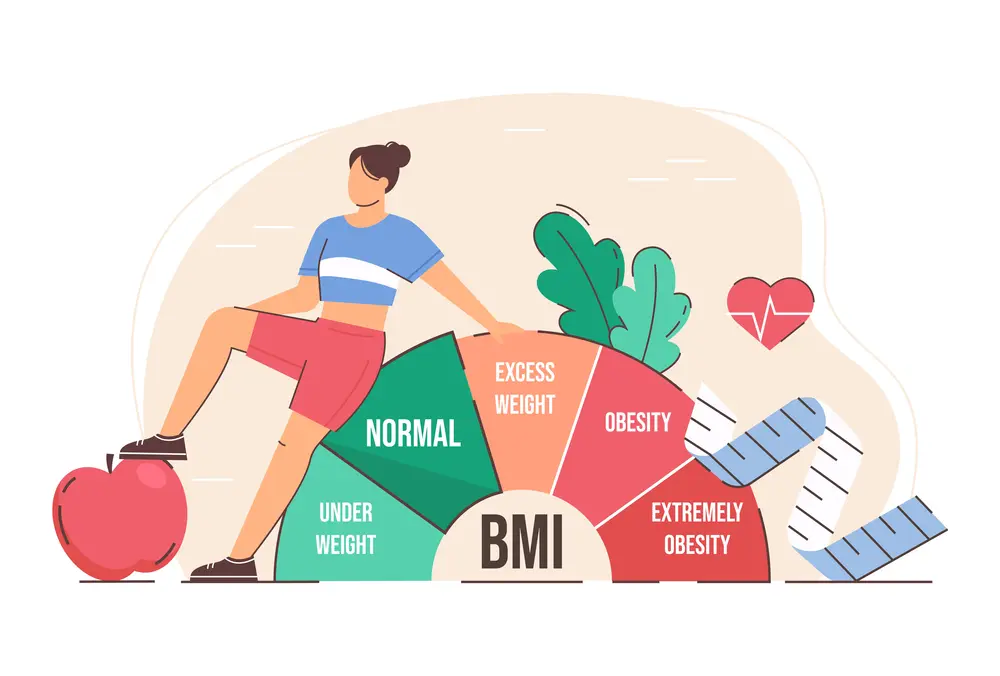
In the realm of weight management, BMI (Body Mass Index) serves as a valuable tool for setting realistic goals and tracking progress toward achieving a healthy weight. By understanding the role of BMI in weight management, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and embark on a journey towards improved well-being.
BMI provides a starting point for individuals to assess their current weight status and determine whether they fall within a healthy range. It acts as a guide, helping individuals set realistic weight loss or weight gain goals based on their unique circumstances. By comparing their current BMI to the recommended healthy BMI range, individuals can gauge the amount of weight they may need to lose or gain to achieve optimal health.
Setting realistic goals is crucial in weight management, as it promotes a sustainable and balanced approach. Rather than aiming for drastic weight changes, which can be challenging to maintain in the long run, individuals can work towards gradual and steady progress. BMI serves as a reference point, allowing individuals to create achievable goals that align with a healthy BMI range. Consulting with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can further enhance the goal-setting process, as they can provide personalized guidance based on individual needs, medical history, and lifestyle factors.
One of the significant advantages of BMI in weight management is its ability to help individuals track their progress over time. By regularly monitoring BMI, individuals can assess how their weight changes align with their goals. It serves as a measurable indicator, enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their health and adjust their strategies if necessary. For instance, if the BMI is not progressing as desired, individuals can review their dietary choices, and physical activity levels, and seek professional guidance to make necessary adjustments and overcome potential barriers.
It is important to note that BMI is not the sole determinant of health, and other factors, such as body composition and overall fitness, should also be considered. Nevertheless, BMI remains a valuable tool in weight management, providing individuals with a tangible way to gauge their progress and make informed decisions about their health.
BMI and Health Risks
Maintaining a balanced BMI (Body Mass Index) is crucial for overall well-being as it helps mitigate potential health risks associated with both high and low BMI values. By understanding the impact of BMI on health, individuals can take proactive measures to achieve and maintain a healthy BMI range, promoting optimal physical and mental well-being.
High BMI values, indicating overweight or obesity, are associated with an increased risk of various health conditions. Research from esteemed sources like the American Heart Association (AHA) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) emphasizes the correlation between high BMI and chronic diseases. Excess weight places strain on the cardiovascular system, leading to an elevated risk of heart disease, hypertension, and stroke. Obesity is also linked to the development of type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, sleep apnea, and musculoskeletal disorders such as osteoarthritis. By maintaining a healthy BMI, individuals can significantly reduce their susceptibility to these health risks and improve their overall quality of life.
On the other hand, having a low BMI, indicating being underweight, also poses health risks. Individuals with low BMI may experience compromised immune function, nutrient deficiencies, and increased vulnerability to infections and illnesses. Low BMI can be indicative of inadequate calorie intake, malnutrition, or underlying medical conditions. It is essential to address low BMI through proper nutrition, balanced diet plans, and medical guidance to achieve a healthy weight and prevent associated health complications.
Maintaining a balanced BMI is crucial as it promotes holistic well-being. A healthy BMI range supports optimal organ function, reduces strain on the cardiovascular system, and enhances metabolic efficiency. It also contributes to improved mental health, self-esteem, and body image. Striving for a balanced BMI through healthy lifestyle choices, including a nutritious diet and regular physical activity, can help individuals achieve and maintain their optimal weight, thereby reducing the risk of chronic diseases and enhancing overall well-being.
BMI as a Screening Tool
BMI (Body Mass Index) serves as a valuable screening tool in healthcare settings, enabling healthcare professionals to identify potential health concerns and initiate necessary interventions. By understanding how BMI is utilized in healthcare, individuals can appreciate its role in the early detection and prevention of various health conditions.
Healthcare professionals often incorporate BMI measurements as part of routine health assessments. BMI is a simple calculation based on an individual’s height and weight, providing an initial indication of overall body composition. It helps healthcare providers assess a person’s weight status and determine if further evaluation is required.
The use of BMI as a screening tool allows healthcare professionals to identify individuals who may be at risk for health conditions related to weight. For example, a high BMI may prompt further investigation for conditions such as obesity, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. This early detection enables healthcare providers to initiate timely interventions, such as lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, physical activity recommendations, and appropriate medical management.
Conversely, a low BMI can also raise concerns for potential health issues such as malnutrition, eating disorders, or underlying medical conditions. Healthcare professionals can use this information as a starting point to delve deeper into an individual’s health status, conduct further assessments, and provide appropriate interventions or referrals to specialists as needed.
It is important to note that BMI is not a definitive diagnostic tool but rather a screening measure that helps identify potential health risks. Additional assessments, such as body composition analysis, medical history evaluation, and laboratory tests, may be necessary to obtain a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s health status.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, maintaining a healthy BMI is vital for overall health and well-being. By utilizing BMI as a screening tool, healthcare professionals can identify potential health concerns and provide timely interventions. This article has emphasized the importance of achieving a balanced BMI range to reduce the risk of chronic diseases and enhance physical and mental well-being. Striving for a healthy BMI through lifestyle choices, such as a nutritious diet and regular exercise, empowers individuals to lead healthier and more fulfilling lives. Prioritizing a balanced BMI is a proactive step towards optimal health and a brighter future.
FAQs
- Why is BMI considered important for health assessments?
- BMI provides a quick and easy way to assess weight status and identify potential health risks associated with different weight categories.
- Can BMI alone determine an individual’s overall health?
- While BMI is a useful indicator, it should be interpreted alongside other health markers and factors to gain a comprehensive understanding of one’s health.
- Are there exceptions where BMI may not accurately reflect an individual’s health status?
- Yes, individuals with high muscle mass or specific medical conditions may have a BMI that does not accurately represent their health status.
- What role does BMI play in weight management?
- BMI serves as a guide for setting weight management goals and monitoring progress toward achieving a healthy weight.
- How often should individuals check their BMI for health maintenance?
- It is recommended to check your BMI periodically, especially when implementing lifestyle changes or engaging in weight management activities, to track progress and make informed decisions about your health.


 Afrikaans
Afrikaans Albanian
Albanian Amharic
Amharic Arabic
Arabic Armenian
Armenian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Basque
Basque Belarusian
Belarusian Bengali
Bengali Bosnian
Bosnian Bulgarian
Bulgarian Catalan
Catalan Cebuano
Cebuano Chichewa
Chichewa Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Traditional)
Chinese (Traditional) Corsican
Corsican Croatian
Croatian Czech
Czech Danish
Danish Dutch
Dutch English
English Esperanto
Esperanto Estonian
Estonian Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish French
French Frisian
Frisian Galician
Galician Georgian
Georgian German
German Greek
Greek Gujarati
Gujarati Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Hausa
Hausa Hawaiian
Hawaiian Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Hmong
Hmong Hungarian
Hungarian Icelandic
Icelandic Igbo
Igbo Indonesian
Indonesian Irish
Irish Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Javanese
Javanese Kannada
Kannada Kazakh
Kazakh Khmer
Khmer Korean
Korean Kurdish (Kurmanji)
Kurdish (Kurmanji) Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz Lao
Lao Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Lithuanian
Lithuanian Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish Macedonian
Macedonian Malagasy
Malagasy Malay
Malay Malayalam
Malayalam Maltese
Maltese Maori
Maori Marathi
Marathi Mongolian
Mongolian Myanmar (Burmese)
Myanmar (Burmese) Nepali
Nepali Norwegian
Norwegian Pashto
Pashto Persian
Persian Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Punjabi
Punjabi Romanian
Romanian Russian
Russian Samoan
Samoan Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic Serbian
Serbian Sesotho
Sesotho Shona
Shona Sindhi
Sindhi Sinhala
Sinhala Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Somali
Somali Spanish
Spanish Sundanese
Sundanese Swahili
Swahili Swedish
Swedish Tajik
Tajik Tamil
Tamil Telugu
Telugu Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Urdu
Urdu Uzbek
Uzbek Vietnamese
Vietnamese Welsh
Welsh Xhosa
Xhosa Yiddish
Yiddish Yoruba
Yoruba Zulu
Zulu