Hey there, health enthusiasts! Are you ready to dive into the world of osmotic diuretics? Get ready to discover a unique approach to managing fluid balance that will leave you amazed. In this article, we’ll take a conversational and engaging journey to explore the fascinating realm of osmotic diuretics.
An osmotic diuretic is a type of medication that increases water excretion more than sodium excretion, helping to maintain urine volume even when the kidney filtration rate is low. It is commonly used to reduce intracranial pressure, lower intraocular pressure, prevent anuria, and promote the excretion of nephrotoxic substances. So, buckle up and get ready to learn about this incredible tool that can make a real difference in our overall health. Let’s delve into the world of osmotic diuretics and uncover the secrets of managing fluid balance like pros!
Understanding Osmotic Diuretics
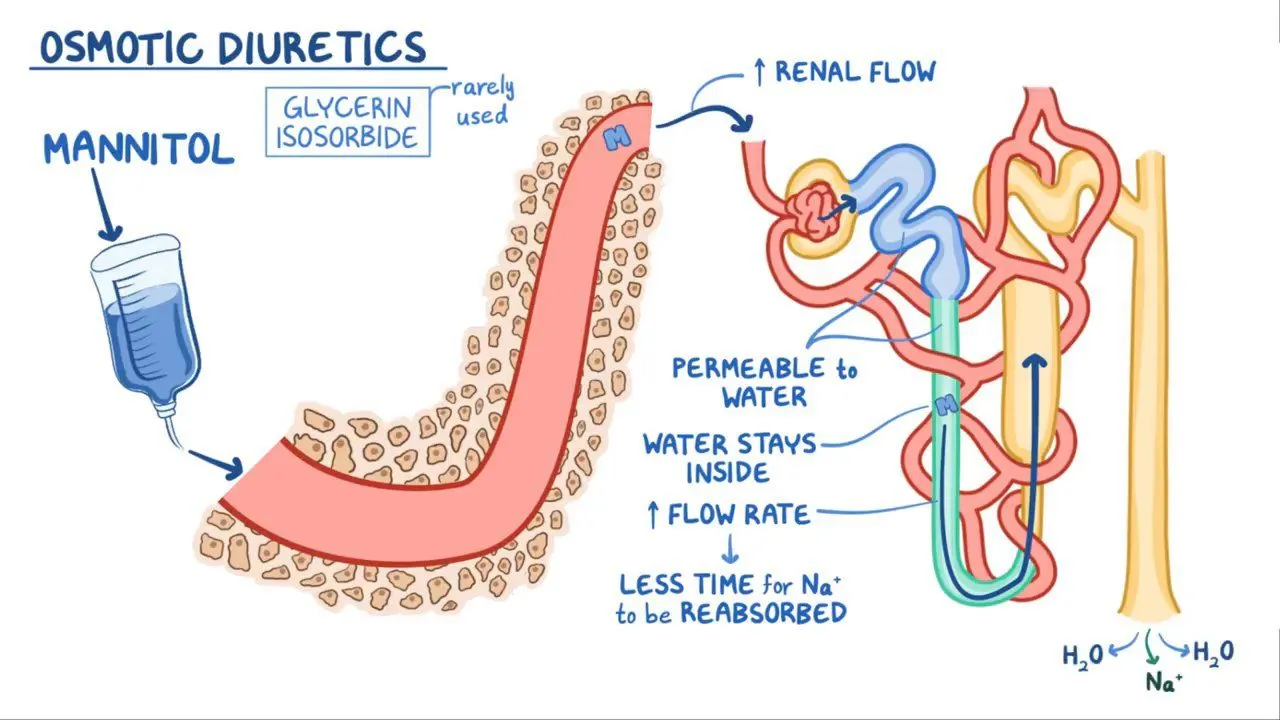
You may be wondering, what exactly are osmotic diuretics? Well, think of them as special medications that have a clever trick up their sleeve. Unlike other diuretics that target specific kidney functions, osmotic diuretics work by creating what we call an osmotic gradient. This gradient helps draw excess water out of our body tissues and into our urine, promoting fluid removal.
Maintaining the right balance of fluids in our bodies is crucial for overall health. When we have too much fluid, it can lead to swelling, edema, and other complications. That’s where osmotic diuretics come into play. They provide a unique approach to managing fluid balance by gently coaxing our bodies to release that extra fluid.
One commonly used osmotic diuretic is called Mannitol. It’s like a superhero that comes to the rescue when fluid overload becomes a concern. Mannitol is particularly effective in treating conditions like cerebral edema (swelling of the brain), acute glaucoma (increased eye pressure), and acute kidney failure. By increasing the osmotic pressure in our kidneys, Mannitol helps remove the excess fluid, bringing relief to those who need it most.
Now, it’s important to note that precise dosing is crucial when it comes to osmotic diuretics. Just like with any medication, getting the right dosage is key. Incorrect dosing can lead to imbalances in electrolytes, dehydration, or excessive fluid loss. That’s why healthcare professionals carefully calculate and administer the appropriate dosage based on individual patient factors. Safety always comes first!
So, there you have it! Osmotic diuretics offer us a unique and effective approach to managing fluid balance. They work by creating an osmotic gradient that helps remove excess fluid from our bodies. Just remember, when it comes to osmotic diuretics, it’s all about finding the right balance and working closely with healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective treatment.
How do osmotic diuretics work?
osmotic diuretics act like magnets for water in your kidneys, pulling them along as they travel through your urinary system. By inhibiting the reabsorption of water in the renal tubules, they help reduce the volume of fluid in your body, making them a valuable tool in managing conditions like edema and hypertension.
Unlike other diuretics that target specific kidney functions, osmotic diuretics work by creating an osmotic gradient. Now, what in the world does that mean? Well, let me break it down for you.
Our body tissues are like sponges, soaking up fluids. Sometimes, in certain medical conditions, too much fluid accumulates in these tissues, leading to swelling and discomfort. That’s where osmotic diuretics come into play. They create an osmotic gradient, which is like a gentle pull that draws excess water out of the tissues and into the urine. It’s like wringing out a wet sponge!
One of the most commonly used osmotic diuretics is Mannitol. It’s like the superhero of the diuretic world. When fluid overload becomes a concern, Mannitol swoops in to save the day. It helps treat conditions like cerebral edema (swelling of the brain), acute glaucoma (increased eye pressure), and acute kidney failure.
So, how does Mannitol create this osmotic gradient? Well, it increases the osmotic pressure in the kidneys, which basically means it creates a higher concentration of particles in the urine. This higher concentration pulls water from the body tissues into the urine, effectively reducing fluid overload.
Uses of Osmotic Diuretics
In the realm of medicine, osmotic diuretics are like versatile artists, with a canvas that includes conditions such as cerebral edema, acute kidney injury, and glaucoma. Their ability to reduce intracranial pressure, increase urine output, and lower intraocular pressure makes them indispensable in various medical scenarios.
Medical conditions requiring osmotic diuretics
From easing the burden on a strained heart to preventing vision loss in glaucoma, osmotic diuretics are superheroes in scenarios where fluid balance is a delicate dance. They’re often prescribed in critical care settings to address emergencies and long-term management of conditions affecting fluid balance.
Types of Osmotic Diuretics
Not all osmotic diuretics are created equal. While mannitol and urea are well-known players in the field, other compounds like isosorbide and hypertonic saline bring their own unique strengths to the table. Each type boasts a specific mechanism of action, catering to different needs within the spectrum of fluid balance regulation.
Overview of different types
Mannitol, with its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, finds its niche in treating cerebral edema, while urea’s cost-effectiveness makes it a popular choice in certain settings. Understanding the distinctions between these types can help healthcare providers tailor treatment strategies to individual patient needs.
Benefits and Risks
Let’s talk about the perks of osmotic diuretics. Besides their efficacy in managing fluid overload, these agents can also improve blood flow to vital organs and reduce the risk of complications in conditions like acute kidney injury. However, like all medications, they come with their own set of risks and side effects, find below more detail.
Benefits:
1. Regulating Fluid Balance: Osmotic diuretics offer an effective means of managing fluid balance in the body. By increasing the osmolarity of the blood, these medications draw excess fluid from tissues and help reduce edema (swelling). This is particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from conditions such as heart failure, kidney disease, or liver cirrhosis.
2. Lowering Intracranial Pressure: Osmotic diuretics can also play a crucial role in reducing intracranial pressure. By reducing the amount of fluid in the brain tissues, these medications aid in the management of conditions like cerebral edema or traumatic brain injury. This benefit can be life-saving, as it helps prevent further damage and improves overall patient outcomes.
3. Kidney Function Support: Osmotic diuretics can support kidney function by promoting diuresis (increased urine production). This can be especially helpful in cases of acute kidney injury or drug overdose, where the clearance of toxic substances is essential for recovery. By enhancing urine output, osmotic diuretics aid in the elimination of waste products and maintain renal health.
Risks:
1. Electrolyte Imbalances: One of the potential risks associated with osmotic diuretics is the development of electrolyte imbalances. These medications can cause the loss of vital electrolytes, such as potassium, sodium, and magnesium. Close monitoring and appropriate supplementation are necessary to prevent complications arising from imbalances, such as muscle weakness, irregular heart rhythms, or even cardiac arrest.
2. Dehydration: Osmotic diuretics can lead to excessive fluid loss, potentially resulting in dehydration. It is important for patients taking these medications to ensure adequate fluid intake to compensate for the increased urine output and prevent dehydration-related complications such as dizziness, dry mouth, or renal dysfunction.
3. Blood Pressure Changes: Osmotic diuretics can affect blood pressure levels. While they can be beneficial in lowering blood pressure in hypertensive patients, they may cause hypotension (low blood pressure) in some individuals. Regular blood pressure monitoring and appropriate dose adjustments are necessary to maintain optimal blood pressure control.
Advantages of using osmotic diuretics
One of the standout benefits of osmotic diuretics is their rapid onset of action, making them invaluable in situations where quick fluid reduction is necessary. Moreover, their ability to improve symptoms and outcomes in conditions like cerebral edema underscores their importance in clinical practice.
Administration and Dosage
Wondering how osmotic diuretics are delivered to the body? Typically administered intravenously, these agents require careful monitoring and dosage adjustments to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of adverse events.
How osmotic diuretics are administered
The intravenous route allows for precise control over the rate and extent of diuresis, ensuring that healthcare providers can tailor treatment to each patient’s unique needs. Close monitoring of urine output, electrolyte levels, and fluid balance is essential to achieving optimal outcomes with osmotic diuretics.
Comparative Analysis
In a world filled with various diuretics, what sets osmotic diuretics apart from the crowd? Unlike thiazides or loop diuretics, osmotic agents work predominantly in the proximal tubule and descending loop of Henle, offering a distinct mechanism of action that can be advantageous in specific clinical scenarios.
Comparing osmotic diuretics with other diuretics
While loop diuretics may be potent in promoting diuresis, their effects can be limited by factors like renal impairment. Osmotic diuretics, on the other hand, can be effective even in compromised kidney function, making them a valuable tool in managing fluid balance in diverse patient populations.
Case Studies
Let’s step into the realm of real-life applications. Meet Sarah, a patient with severe cerebral edema whose condition improved dramatically with the judicious use of mannitol. By reducing intracranial pressure and improving cerebral perfusion, osmotic diuretics like mannitol can be game-changers in critical care scenarios.
Real-life applications and success stories
From preventing vision loss in patients with glaucoma to mitigating brain swelling in traumatic brain injury, osmotic diuretics have left their mark on numerous medical success stories. These case studies highlight the vital role that these agents play in managing fluid balance disorders.
Research and Development
As science marches forward, so does the realm of osmotic diuretics. Ongoing research aims to uncover new applications, refine dosing strategies, and explore novel formulations that can enhance the safety and efficacy of these agents. The future holds exciting possibilities for improving fluid balance management through innovation in osmotic diuretic therapy.
Advances in osmotic diuretic research
Recent studies have delved into the use of osmotic diuretics in conditions like acute respiratory distress syndrome and liver cirrhosis, showcasing the expanding scope of their utility. By delving deeper into their mechanisms and exploring new avenues for application, researchers are paving the way for better outcomes in fluid balance disorders.
Precautions and Contraindications
While osmotic diuretics are powerful tools, they’re not without their caveats. Patients with certain medical conditions, such as dehydration or heart failure, may need to steer clear of these agents to prevent further complications. Understanding the risks and contraindications associated with osmotic diuretics is vital for safe and effective treatment.
Who should avoid osmotic diuretics?
Individuals with a history of electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, or hypersensitivity to osmotic diuretics should exercise caution when considering these agents as part of their treatment plan. Healthcare providers play a key role in identifying patients who may not be suitable candidates for osmotic diuretic therapy.
Combination Therapy
In the world of medicine, collaboration is key. Pairing osmotic diuretics with other treatment modalities, such as anti-hypertensives or diuretics from different classes, can enhance their efficacy and address multiple aspects of fluid balance regulation simultaneously.
Using osmotic diuretics in combination with other treatments
By leveraging the strengths of different medications in a coordinated approach, healthcare providers can optimize patient outcomes and minimize the risk of adverse effects. The synergy between osmotic diuretics and complementary therapies underscores the importance of a holistic treatment strategy in managing fluid balance disorders.
Cost and Accessibility
Let’s talk dollars and sense when it comes to osmotic diuretics. The affordability and accessibility of these medications are significant factors that influence their use in healthcare settings.
Affordability of Osmotic Diuretics
Keeping the budget in check is crucial for both patients and healthcare systems. While osmotic diuretics offer valuable benefits in managing fluid balance disorders, considerations about their cost-effectiveness can impact treatment decisions. Understanding the financial implications of using osmotic diuretics can help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans that align with patients’ financial capabilities.
Accessibility of Osmotic Diuretics
Having access to necessary medications is a fundamental right for all individuals. Ensuring the availability of osmotic diuretics in healthcare facilities, pharmacies, and formularies plays a pivotal role in delivering equitable care. By addressing concerns related to supply chain management, formulary restrictions, and insurance coverage, healthcare providers can work towards enhancing access to osmotic diuretics for those who stand to benefit from their therapeutic effects.
Expert Opinions
Let’s hear from the experts in the field. Healthcare professionals who work closely with osmotic diuretics bring a wealth of experience and insights to the table, offering valuable perspectives on their use, benefits, and potential pitfalls.
Insights from healthcare professionals
From nephrologists to intensivists, experts highlight the nuanced considerations that go into selecting and dosing osmotic diuretics. Their firsthand experiences shed light on best practices, emerging trends, and areas for future exploration in osmotic diuretic therapy.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our deep dive into the realm of osmotic diuretics, it’s clear that these agents play a crucial role in managing fluid balance with finesse and precision. From their unique mechanism of action to their diverse applications in clinical practice, osmotic diuretics stand out as valuable tools in the healthcare toolkit. By understanding their benefits, risks, and optimal use, healthcare providers can harness the power of osmotic diuretics to improve patient outcomes and enhance the quality of care.
FAQs
1. Are osmotic diuretics safe for long-term use?
- Osmotic diuretics can be used safely for extended periods under proper medical supervision. However, close monitoring is essential to prevent adverse effects.
2. Can osmotic diuretics be used in pediatric patients?
- Osmotic diuretics have applications in pediatric care, but dosing and monitoring considerations may vary based on age and weight.
3. Do osmotic diuretics interact with other medications?
- Osmotic diuretics can interact with certain medications, so it’s important to inform your healthcare provider about all the drugs you’re taking.
4. How quickly do osmotic diuretics start working?
- Osmotic diuretics typically have a rapid onset of action, with effects seen within minutes to hours after administration.
5. Can osmotic diuretics cure fluid balance disorders?
- While osmotic diuretics are effective in managing fluid balance, they are usually part of a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to each individual’s needs.
With the versatility and efficacy of osmotic diuretics, the healthcare landscape continues to benefit from their unique approach to fluid balance management. By staying informed, engaging in dialogue with healthcare providers, and advocating for personalized care, individuals can navigate the complex terrain of fluid balance with greater confidence and knowledge. Here’s to a balanced, hydrated, and healthy future for all!


 Afrikaans
Afrikaans Albanian
Albanian Amharic
Amharic Arabic
Arabic Armenian
Armenian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Basque
Basque Belarusian
Belarusian Bengali
Bengali Bosnian
Bosnian Bulgarian
Bulgarian Catalan
Catalan Cebuano
Cebuano Chichewa
Chichewa Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Traditional)
Chinese (Traditional) Corsican
Corsican Croatian
Croatian Czech
Czech Danish
Danish Dutch
Dutch English
English Esperanto
Esperanto Estonian
Estonian Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish French
French Frisian
Frisian Galician
Galician Georgian
Georgian German
German Greek
Greek Gujarati
Gujarati Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Hausa
Hausa Hawaiian
Hawaiian Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Hmong
Hmong Hungarian
Hungarian Icelandic
Icelandic Igbo
Igbo Indonesian
Indonesian Irish
Irish Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Javanese
Javanese Kannada
Kannada Kazakh
Kazakh Khmer
Khmer Korean
Korean Kurdish (Kurmanji)
Kurdish (Kurmanji) Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz Lao
Lao Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Lithuanian
Lithuanian Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish Macedonian
Macedonian Malagasy
Malagasy Malay
Malay Malayalam
Malayalam Maltese
Maltese Maori
Maori Marathi
Marathi Mongolian
Mongolian Myanmar (Burmese)
Myanmar (Burmese) Nepali
Nepali Norwegian
Norwegian Pashto
Pashto Persian
Persian Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Punjabi
Punjabi Romanian
Romanian Russian
Russian Samoan
Samoan Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic Serbian
Serbian Sesotho
Sesotho Shona
Shona Sindhi
Sindhi Sinhala
Sinhala Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Somali
Somali Spanish
Spanish Sundanese
Sundanese Swahili
Swahili Swedish
Swedish Tajik
Tajik Tamil
Tamil Telugu
Telugu Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Urdu
Urdu Uzbek
Uzbek Vietnamese
Vietnamese Welsh
Welsh Xhosa
Xhosa Yiddish
Yiddish Yoruba
Yoruba Zulu
Zulu