Introduction: The Midnight Bathroom Trips
Do you find yourself waking up multiple times during the night to use the bathroom? If so, you’re not alone. Nocturia, the medical term for excessive urination at night, can be an inconvenient and disruptive issue that affects many individuals. While occasional nighttime urination is normal, frequent trips to the bathroom can significantly impact your sleep quality and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore seven common reasons why you might be experiencing nocturia and provide effective solutions to help you regain uninterrupted sleep.
1. Increased Fluid Intake
One of the most common reasons for frequent urination at night is increased fluid intake before bedtime. Drinking too much water or other fluids before going to bed can cause your bladder to fill up faster, leading to the need to urinate more frequently. While it’s important to stay hydrated throughout the day, it’s recommended to limit fluid intake a few hours before bedtime to reduce the risk of nocturia. Additionally, avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and other diuretics can also help reduce the need for nighttime urination. Making simple adjustments to your daily routine, such as adjusting your fluid intake and avoiding certain beverages, can significantly improve your sleep quality and overall health.
2. Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder is a common condition that can affect both men and women, causing frequent urges to urinate, including at night. This condition is caused by involuntary contractions of the bladder muscles, which can result in the need to urinate even when the bladder isn’t full. If you’re experiencing symptoms of an overactive bladder, such as frequent nighttime trips to the restroom, it’s important to seek management strategies. Treatment options may include medications to help relax the bladder muscles, behavioral therapies to help train the bladder to hold more urine, or even surgery in severe cases. With proper management, an overactive bladder can be effectively controlled, allowing you to regain control over your bladder and enjoy a better quality of life.
3. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
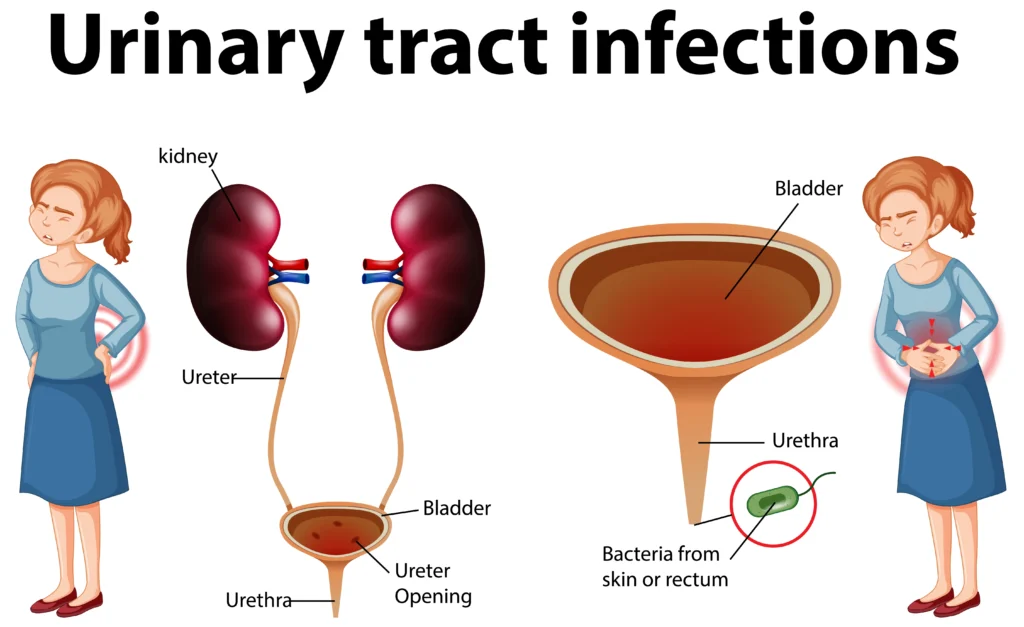
Tract Infections (UTIs) can be a contributing factor to nocturia, the need to urinate frequently at night. Chronic UTIs, which are recurring or persistent infections in the urinary tract, can disrupt the normal functioning of the bladder and lead to increased nighttime urination. It is crucial to seek proper treatment and prevention methods for UTIs to address this issue. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat UTIs and eliminate the infection-causing bacteria. Additionally, maintaining good hygiene practices, staying hydrated, and regularly can help prevent UTIs from occurring or recurring. Suppose you are experiencing frequent nighttime urination and suspect a UTI. In that case, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment to alleviate the symptoms and prevent further complications.
4. Prostate Enlargement (in Men)
Prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), can cause disruptions in normal bladder function, leading to frequent nighttime urination in men. As the prostate gland grows in size, it can squeeze the urethra, the tube responsible for urine flow, causing urinary symptoms such as increased frequency and urgency. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance. They can provide a comprehensive assessment, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatment options to manage the symptoms. Treatment may include medication to shrink the prostate or relieve urinary symptoms, lifestyle modifications, or in some cases, surgical intervention. Seeking medical advice will help address the underlying cause of nighttime urination and improve your overall urinary health.
5. Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that can lead to a range of complications, including increased urine production and frequent nighttime urination. High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, which are vital in filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. As a result, the kidneys may become less effective at regulating fluid balance, leading to increased urine production and a greater need to urinate, especially at night. Proper management of diabetes is essential to prevent or manage these symptoms. This may involve monitoring blood sugar levels, taking medications as prescribed, adopting a healthy diet and exercise regimen, and making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking or reducing alcohol intake. By managing diabetes effectively, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve their overall health and quality of life.
6. Medications
Certain medications, including diuretics, can increase urine production and lead to frequent urination, especially at night. While these drugs can be effective in treating various conditions such as high blood pressure or heart failure, they can also cause unwanted side effects. If you are experiencing frequent nighttime urination as a result of medication use, it is important to discuss alternatives with your doctor. They can evaluate your overall health and medical history and recommend alternative medications or treatment options that may be less likely to cause urinary symptoms. In some cases, adjusting the timing or dosage of medication may also help alleviate symptoms. It is important to always consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your medication regimen to ensure safe and effective treatment.
7. Sleep Disorders

Sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea, insomnia, or restless leg syndrome can contribute to the occurrence of nocturia, which is the need to urinate frequently during the night. These conditions can disrupt normal sleep patterns and affect the quality of sleep, leading to increased awakenings and a heightened urge to urinate. It is important to address and manage the underlying sleep issues to alleviate the symptoms of nocturia.
For obstructive sleep apnea, treatment options may include lifestyle changes, the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices, or surgical interventions to improve breathing during sleep. Insomnia can be managed through cognitive behavioral therapy, sleep hygiene practices, or medications prescribed by a healthcare professional. Restless leg syndrome may be relieved through lifestyle modifications, medications, or other therapies aimed at reducing the discomfort and sensations in the legs.
By effectively managing and treating sleep disorders, individuals can improve the quality of their sleep, reduce nocturia episodes, and enhance overall well-being. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss symptoms, undergo appropriate evaluations, and develop a personalized treatment plan to address any underlying sleep issues.
Conclusion
Experiencing frequent peeing at night, also known as nocturia, can be bothersome and disruptive to sleep. However, there are several reasons as we discussed above, and addressing them can help alleviate the issue. By implementing lifestyle changes, seeking medical advice, and addressing underlying conditions, individuals can take steps to fix nocturia and improve their quality of sleep.
FAQs
1. Why do I pee so much at night?
– Nocturia can be caused by various factors, including excessive fluid intake, urinary tract infections, certain medications, and medical conditions such as diabetes or bladder problems. Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause.
2. How can I reduce nighttime urination?
– To reduce nighttime urination, it’s recommended to limit fluid intake before bed, avoid caffeine and alcohol, practice good sleep hygiene, and address underlying health issues. Additionally, consulting a healthcare provider for further evaluation and management is advisable.
3. Can anxiety or stress cause nocturia?
– Yes, anxiety and stress can contribute to nocturia. These emotional factors can disrupt sleep patterns and increase the frequency of nighttime urination. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, therapy, or counseling may help alleviate the issue.
4. Is nocturia a sign of a serious medical condition?
– Nocturia can be a symptom of various medical conditions, including urinary tract infections, diabetes, kidney problems, or prostate issues. While it may not always indicate a serious condition, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
5. Are there any lifestyle changes that can help with nocturia?
– Yes, there are lifestyle changes that can help manage nocturia. These include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, avoiding excessive fluid intake before bed, and emptying the bladder before sleeping. Additionally, seeking medical advice and following recommended treatment plans are crucial for addressing underlying causes.
Remember, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding any health concerns or persistent symptoms.


