Understanding the key clinical symptoms associated with hypothyroidism is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. If you are feeling persistently tired, experiencing unexplained weight gain, and noticing changes in your skin and hair health? These could be potential signs of an underactive thyroid gland, a condition known as hypothyroidism. In this article, we will explore the four major clinical symptoms of hypothyroidism and delve into their impact on your health and well-being.
Introduction
Hypothyroidism refers to an insufficient production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland, leading to a decline in their circulation throughout the body. The thyroid hormones primarily control the body’s metabolism, influencing energy production, weight regulation, and many vital functions. Recognizing the clinical symptoms associated with hypothyroidism is essential for seeking appropriate medical intervention and ensuring optimal thyroid function.
The Thyroid Gland and Its Functions
Before exploring the clinical symptoms of hypothyroidism, let’s briefly understand the crucial role of the thyroid gland. Located in the neck, the thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones, such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are responsible for regulating the body’s metabolism. These hormones help determine the rate at which calories are burned, affecting energy levels and overall well-being.
Major Clinical Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism manifests in various ways, impacting different aspects of daily life. Let’s delve into the four major clinical symptoms associated with this condition:
1. Fatigue and Weakness
One of the most prominent symptoms of hypothyroidism is fatigue and an overall feeling of weakness. The thyroid hormone plays a vital role in regulating the body’s metabolism, impacting energy production. When the thyroid gland becomes underactive, it hampers the energy conversion process, leading to a persistent lack of energy.
Individuals with hypothyroidism often find themselves battling through daily tasks, experiencing a constant sense of exhaustion. Simple activities that were once effortless may now require significant effort and leave them feeling drained. Managing fatigue through lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, is essential for individuals with hypothyroidism.
2. Weight Gain
Weight gain is another common clinical symptom associated with hypothyroidism. The thyroid hormone plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, which affects how efficiently the body burns calories. When the thyroid gland is underactive, the metabolic rate slows down, leading to weight gain.
Individuals with hypothyroidism often struggle with unexplained and stubborn weight gain, even when they consume a balanced diet or exercise regularly. The weight gain is typically gradual and might be accompanied by difficulty in losing weight despite efforts to do so. Managing weight through a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, and potential medication is important for individuals with hypothyroidism.
3. Dry Skin and Hair Loss
Hair loss and dry skin are common symptoms experienced by individuals with hypothyroidism. The thyroid hormone influences the health and growth of hair follicles and skin cells. Insufficient thyroid hormone levels can disrupt this balance, leading to hair thinning, brittle hair, and dry, itchy skin.
People with hypothyroidism may notice an increased amount of hair shedding, especially when brushing or washing their hair. Additionally, their skin may become dry, rough, and prone to flaking. Proper skincare, including moisturizing techniques and products, as well as using gentle hair care practices, can help manage these symptoms.
4. Cold Sensitivity
Cold sensitivity is a notable symptom among those with hypothyroidism. The thyroid hormone plays a role in regulating body temperature and thermoregulation. When the thyroid is underactive, individuals may experience heightened sensitivity to cold temperatures.
People with hypothyroidism might find themselves feeling cold even in comfortable room temperatures, needing extra layers of clothing to stay warm. Cold intolerance can significantly impact their daily lives, making them susceptible to discomfort and affecting their overall well-being. Wearing suitable clothing, using warm blankets, and ensuring proper heating are practical ways to alleviate this symptom.
Fatigue and Sluggishness
Hypothyroidism-induced fatigue and sluggishness can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. Simple daily activities may become arduous tasks, and concentration and productivity can diminish. The decline in thyroid hormone levels reduces the body’s metabolic activity, including the rate at which energy is produced. As a result, individuals with hypothyroidism may constantly feel drained and require more rest to recover.
Weight Gain and Difficulty Losing Weight
Overcoming weight challenges poses a significant hurdle for individuals with hypothyroidism. The slowdown in metabolic processes, attributed to reduced thyroid hormone levels, limits the body’s ability to burn calories efficiently. This diminished calorie-burning capacity makes it easier to gain weight, even with a controlled diet. Additionally, shedding excess weight becomes increasingly difficult, as the body’s metabolism struggles to respond to dietary and exercise interventions.
Dry Skin and Hair Loss
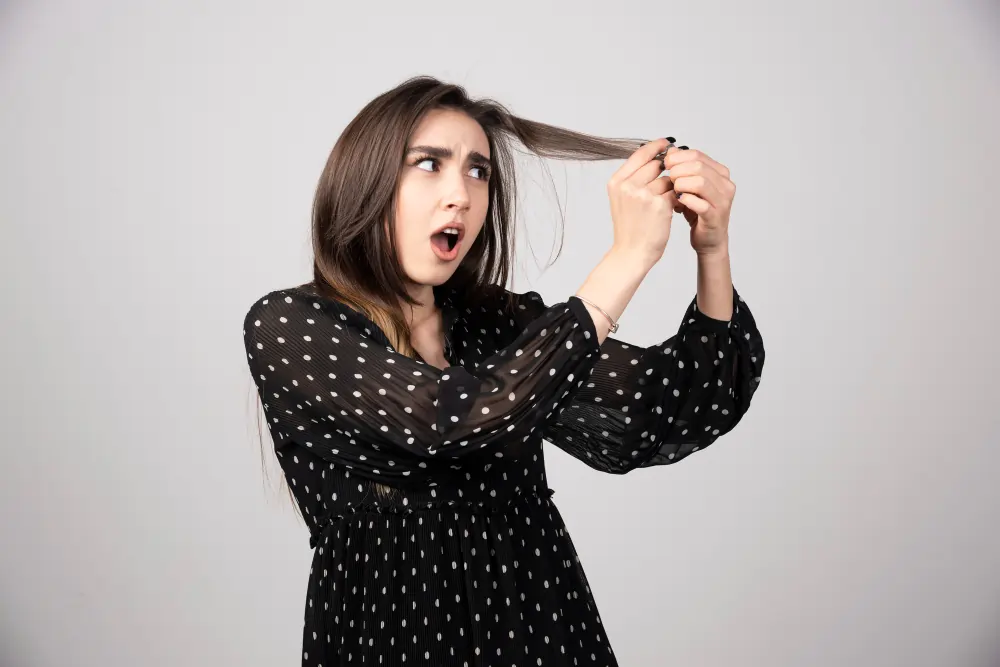

Inadequate thyroid hormone levels can have adverse effects on the health of your skin and hair. The skin requires optimal thyroid hormone levels to retain moisture effectively. When these hormone levels drop, the skin can become dry, scaly, and prone to irritation. Similarly, hair follicles depend on adequate hormone levels for strength and growth. In hypothyroidism, diminished hormone production can lead to hair becoming brittle, thin, and more prone to breakage, resulting in noticeable hair loss.
Feeling Cold All The Time
The impaired regulation of body temperature due to hypothyroidism can cause individuals to feel persistently cold, even in moderate environments. Thermoregulation, the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal temperature, is influenced by thyroid hormones. By controlling the basal metabolic rate, these hormones help generate heat to keep the body warm. When thyroid hormone levels are low, the body’s thermoregulation mechanism can be compromised, making individuals with hypothyroidism feel cold and uncomfortable in relatively cool surroundings.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hypothyroidism
Diagnosing hypothyroidism involves a combination of clinical assessment and laboratory tests. A healthcare professional will evaluate the clinical symptoms, medical history, and physical examination findings to determine the likelihood of hypothyroidism. A blood test measuring the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones, T3 and T4, is often conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
Once diagnosed, treatment typically involves synthetic hormone replacement therapy. Synthetic thyroid hormones effectively supplement the inadequate production of natural hormones, restoring optimal thyroid function. Regular monitoring of hormone levels through follow-up blood tests is essential to ensure the dosage of medication is adjusted as needed.
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Identifying and managing hypothyroidism in its early stages is vital to prevent complications and maintain a good quality of life. Left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to several long-term health issues, including cardiovascular problems, infertility, depression, and cognitive decline. Prompt treatment helps alleviate symptoms, balances metabolism, and minimizes the risk of developing more severe complications.
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism, characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, presents with various clinical symptoms that significantly impact an individual’s well-being. Recognizing and understanding these symptoms, including fatigue and sluggishness, weight gain and difficulty losing weight, dry skin and hair loss, as well as feeling cold all the time, is crucial for early detection and effective management. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment can enhance your overall quality of life and mitigate potential long-term complications associated with hypothyroidism.
FAQs
1. What causes hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism can be caused by autoimmune diseases, certain medications, radiation therapy, thyroid surgery, and congenital factors. The most common cause is an autoimmune condition called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
2. Is hypothyroidism a reversible condition?
While hypothyroidism is typically a lifelong condition, with the right treatment and medication, individuals can effectively manage the symptoms and lead a normal life.
3. Can hypothyroidism lead to weight gain?
Yes, hypothyroidism can lead to weight gain due to its impact on the body’s metabolic rate and calorie-burning capacity.
4. Are there any natural remedies for hypothyroidism?
While there is no natural remedy that can cure hypothyroidism, certain lifestyle changes like eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and minimizing stress can support overall thyroid health.
5. How long does it take to see improvement with treatment?
Individual response to treatment can vary, but most individuals start experiencing improvements in their symptoms within a few weeks of starting hormone replacement therapy. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to monitor progress and adjust medication dosage as needed.